![[Warning]](/media/com_docimport/admonition/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
|
If you backup and restore your site on a new host you MUST change these configuration parameters to reflect your new server configuration manually. In fact, you must remove your .htaccess file, let WordPress regenerate a new .htaccess files, then let Admin Tools create a new .htaccess file before you can use your site's front-end. |
Optimisation and utility
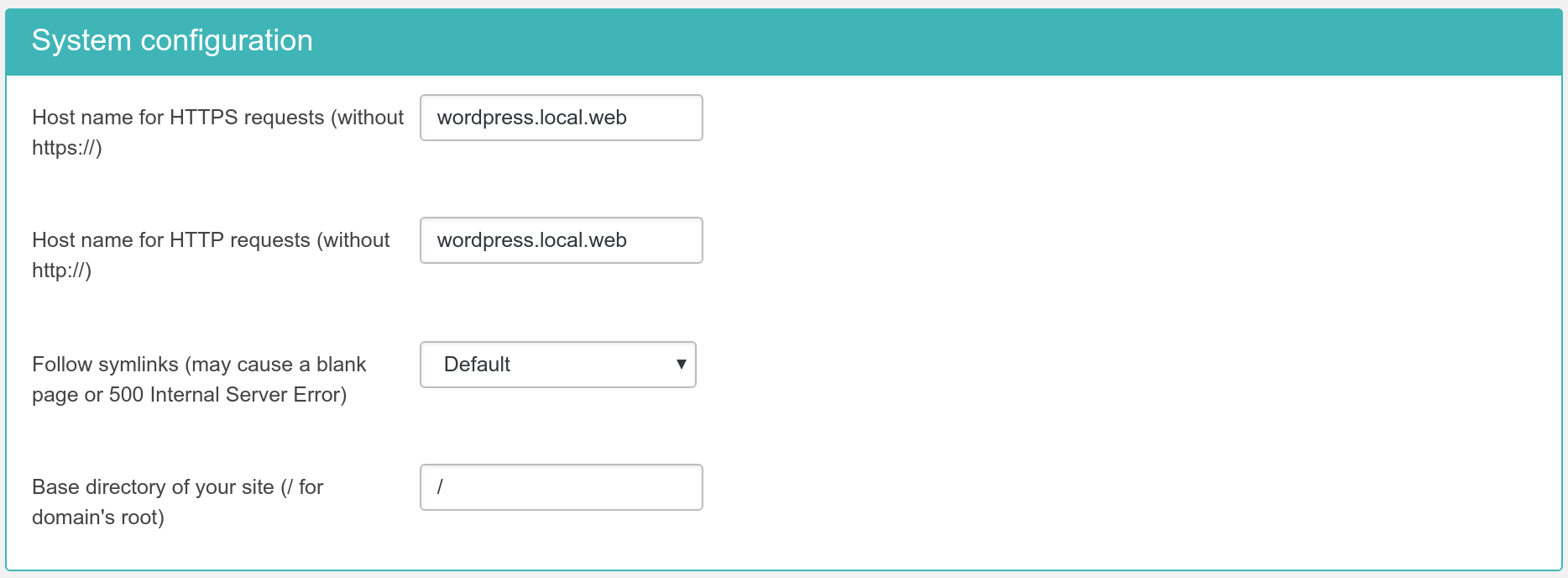
This final section contains all the options which let the .htaccess maker know some of the most basic information pertaining your site and which are used to create the rules for some of the options in the previous section.
- Host name for HTTPS requests (without https://)
-
Enter the site's domain name for secure (HTTPS) connections. By default, Admin Tools assumes it is the same as your site's domain, but you have to verify it as it may be different on some hosts, especially on shared hosts. Do not use the https:// prefix, just the domain name without the path to your site. For example, if the address is
https://www.example.com/wordpressthen type inwww.example.com. - Host name for HTTP requests (without http://)
-
Enter the site's domain name for regular (HTTP) connections. By default, Admin Tools assumes it is the same as the address you are connected to right now, but you have to verify it. Do not use the http:// prefix, just the domain name without the path to your site. For example, if the address to your site's root is
http://www.example.com/wordpressthen type inwww.example.com. - Follow Symlinks
-
WordPress normally does not create symlinks and does not need symlinks. At the same time, hackers who have infiltrated a site do use symlinks to get read access to files that are normally outside the reach of the web site they have hacked. This is why this option exists. You can set it to:
-
Default. It's up to your host to determine if symlinks will be followed. Use this if the other options cause problems to your site.
-
Yes, always. This is the insecure option. If you use it keep in mind that in the event of a hack all world-readable files on the server may be compromised. Really, it's a horrid idea. Don't use it.
-
Only if owner matches. That's the safe approach to enabling symlinks. They will be followed only if the owner of the symlink matches the owner of the file/directory it links to.
If you have no idea what that means, first try setting this option to "Only if owner matches". If this results in a blank page or an Internal Server Error 500 then set this to "Default". For more information please consult Apache's documentation.
-
- Base directory of your site
-
This is the directory where your site is installed. For example, if it is installed in a directory named
wordpressand you access it on a URL similar tohttp://www.example.com/wordpressyou have to type in/wordpressin here. If your site is installed on the root of your domain, please use a single forward slash for this field:/